Co-authored by Jeffrey Ellin, Solutions Architect, Qubole.
Serverless architecture allows you to execute code without requiring the traditional cost of compute resources. Each component of your application exists independently in the cloud and only consumes resources when they are being executed. They can be scaled easily and due to their ephemeral nature you only pay for what you use. Due to the way they are deployed they discourage the use of bad habits when implementing microservice architectures.
AWS’s Lambdas are an ideal fit for implementing a serverless architecture. They are single units of functionality that are deployed to the cloud and are executed in response to events that occur inside the cloud.
These events can include:
- Changes to Objects in S3
- Messages placed on a queue
- Invocation by Data Pipelines
- Invocation by Amazon API Gateway
Lambdas can be written in a variety of languages including Java, Python and Node.js. Amazon allows you to package dependencies and publish them via APIs which makes makes them ideal for a Continuous Integration/Deployment scenarios.
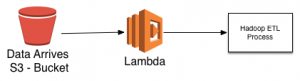
In the big data landscape, Lambdas can be used to facilitate Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) workloads in response to a new dataset being placed in S3. In a traditional on-premise scenario there needs to be a dedicated set of resources that are always on and ready to perform these workloads. Cluster scaling must be done for the worst case scenario. This inelasticity is expensive and to expand when they become oversubscribed. With a Lambda function, we can scale up the required resources as a result of the files being ready to processed. When we are done, the cluster resources will be scaled down. If we have uneven needs for compute, such as end of quarter processing, we will only pay for our resources when they’re actually utilized.In this blog post, I will talk about how to implement an ETL pipeline with an AWS Lambda function and the Qubole Data Service (QDS) platform.
QDS platform can eliminate the need for configuring a static sized Hadoop cluster to perform ETL or other Spark workflows. Upon invocation of the API, QDS will start the cluster and scale it appropriately. Once the workload is complete the cluster will be scaled down or shut down.
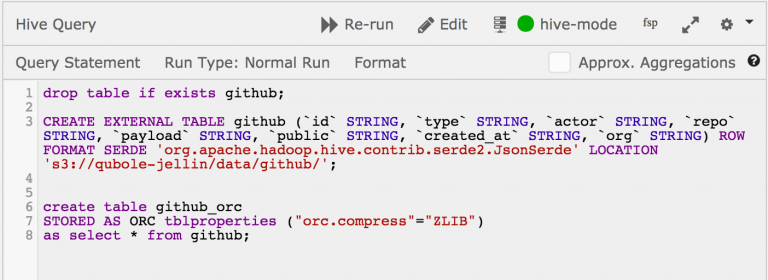
The following Hive SQL will be run as a response to new data arriving in S3 bucket.
drop table if exists github;CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE github(`id` STRING,`type` STRING,`actor` STRING,`repo` STRING,`payload` STRING,`public` STRING,`created_at` STRING,`org` STRING)ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.JsonSerde' LOCATION 's3://data/github/';create table github_orcSTORED AS ORC tblproperties ("orc.compress"="ZLIB")as select * from github;
Data is ephemeral to the cluster as it is stored in S3. This is true for both the external table GitHub and the hive managed table github_orc. The cluster can be completely shut down and we will not lose any of the stored data. The data set we received in this example is a large JSON gzip file. This is a poor file format for ad-hoc querying. ORC or Parquet with a splittable compression format is a much better choice.Although, we could use other tools such as Spark or Pig to do this, we are going to use Hive for its simplicity.
The following Lambda invokes the Hive workload on the Qubole Platform.
from qds_sdk.qubole import Qubolefrom qds_sdk.qubole import Qubolefrom qds_sdk.commands import HiveCommandimport qds_sdk.exceptionfrom qds_sdk.util import GentleOptionParserimport sysimport tracebackimport loggingimport shleximport jsonlog = logging.getLogger("mr_1")api_token = "xyz"Qubole.configure(api_token=api_token)def lambda_handler(event, context):logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)upload()def upload():script_location = "s3://scripts/test.sql"args = shlex.split('run --script_location %s'% (script_location))args2 = HiveCommand.parse(args)cmd = HiveCommand.create(**args2)print(("HiveCommand Job run via command id: %s, finished with status %s"% (cmd.id, cmd.status)))
Viewing the result in Qubole
The result of this rather simple code is that we have a compute cluster that can execute our ETL workload whenever a new file arrives. If files arrive infrequently, we pay zero dollars to host this infrastructure, but when year end processing time comes around we can scale up with zero user intervention.
If you’re interested in QDS, sign up today for a free trial! To get an overview of QDS, click here to register for a live demo.